题目:城市公园设施与老年使用者体力活动强度--基于GPS与体力活动强度仪综合数据
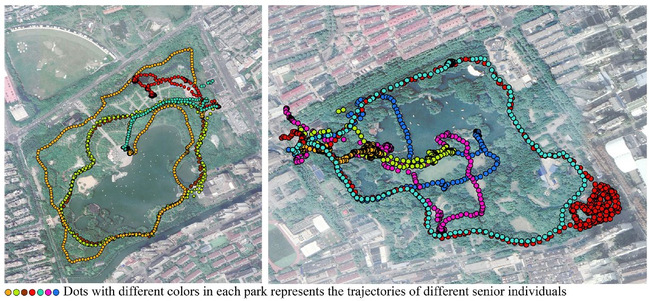
摘要:Physical activity provides multiplehealth benefits to seniors, and urban parksare one of theprimary settings whereseniors engage in physical activity. However,seniors' park-based physical activity andtheir needs related to park environmentalcharacteristics are not well understood. Thisstudy aimed to explore associationsbetween the intensity of seniors' physicalactivity during park visits and the types ofpark facilities (e.g. pathways, lawns) theyuse. We recruited seniors from two parks inShanghai at the beginning of their parkvisits, and used ac-celerometers to assessinstantaneous metabolic equivalent ofenergy (MET) along with GPS to trackspatial locations of these activities at 10-second intervals . Data from 286participants were included, and we than 3.5 m, pathway narrower than 3.5 m,large paved open space, small paved openspace, sports area, children's playground,lawn, water, other natural area, andbuilding and other area. A multilevellogistic model was built with type of facilityas the independent variable andinstantaneous physical activity intensity asthe outcome variable. We also appliedstepwise regression analyses to examinethe relationship between the proportion oftime spent in moderate and vigorousphysical activity (MVPA), overall MET(dependent variable), and the proportion oftime spent using different park facilities.
主编:CAUP学院科研管理部审阅:赫 磊
采编:张玉婷
编辑:吕 正
排版:林诗佳
校对:单 霞
全文附后,链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169204619315385?via%3Dihub